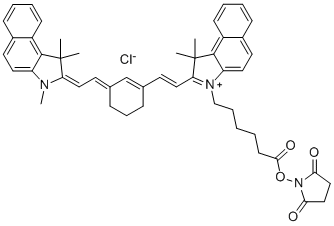
Cy7.5-N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺酯
货号:AGF1356A-25mg
包装:25mg
包装:25mg
</

</
| 订购货号 | 产品名称及规格 |
| 16020 | Cyanine7.5 NHS ester, 1 mg |
| 26020 | Cyanine7.5 NHS ester, 5 mg |
| 46020 | Cyanine7.5 NHS ester, 25 mg |
| 56020 | Cyanine7.5 NHS ester, 50 mg |
| 66020 | Cyanine7.5 NHS ester, 100 mg |
Cyanine7.5是一种近红外荧光染料,具有很长的发射光谱,是此类荧光衍生而来的活性胺产品。
General properties
| Appearance: | green powder |
| Molecular weight: | 782.41 |
| Molecular formula: |
C49H52ClN3O4 |
| Solubility: | soluble in organic solvents (DMSO, DMF, dichloromethane), low solubility in water |
| Quality control: | NMR 1H (95%) and 13C, TLC, functional testing |
| Storage conditions: | Storage: 24 months after receival at -20°C in the dark. Transportation: at room temperature for up to 3 weeks. Avoid prolonged exposure to light. Desiccate. |
| MSDS: | Download |
Spectral properties
| Excitation maximum, nm: | 788 |
| Extinction coefficient at excitation maximum, Lmol-1cm-1: | 223000 |
| Emission maximum, nm: | 808 |
</